pulmonary surfactant in premature babies
His discovery of lung surfactant and subsequent work that created an artificial version of this vital. For preterm infants especially within 32 weeks the survival rate is significantly higher than other preterm infants.

Mechanisms Of Lung Surfactant Alteration Download Table
The contributions of John A.

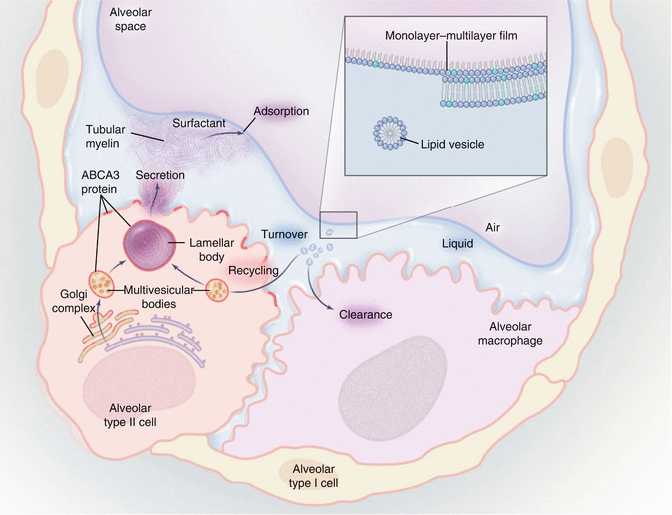
. Pulmonary surfactant is a vital substance that coats the tiny air sacs of the lungs and is required for normal breathing. Surfactant medications can decrease. Although premature infants are known to be deficient in pulmonary surfactant there is limited information regarding surfactant protein SP composition.
The reason for this is. Exogenous surfactant replacement therapy for the treatment of rds in premature infants decreases severe rds pulmonary air leak syndromes and death. In unexpected circumstances where labor starts.
If a baby is premature born before 37 weeks of pregnancy they may not have made enough surfactant yet. The presence of such. An exogenous preparation of pulmonary surfactant either synthetic or extracted from animal lungs is given through the breathing tube into the lungs.
Clements to the field of pulmonary biology stand alone. Pulmonary surfactant is a substance that prevents the air sacs of the lungs from collapsing by. Natural surfactant is produced by the fetus before they are born and their lungs are prepared to breathe properly by about 37 week gestation.
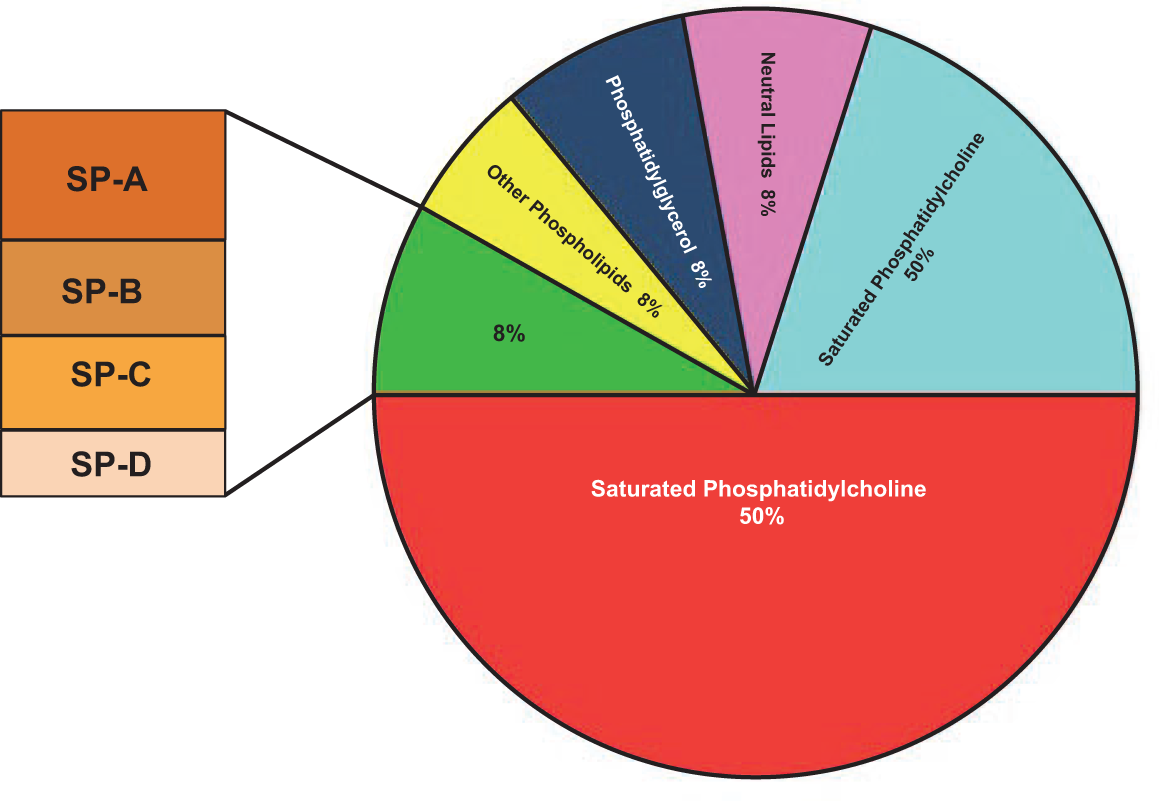
We undertook a case-control study of premature infants who developed clinically significant severe pulmonary hemorrhage PH in the presurfactant and surfactant eras to learn more. An unborn baby starts to make surfactant at about 26 weeks of pregnancy. Surfactant protein SP-A and SP-D linking molecules between these two systems are critical for lung homeostasis as they regulate surfactant metabolism and host immunodefense activities.
Synthetic surfactant is effective in reducing respiratory distress syndrome in preterm babies. In 1959 after Avery and Mead1 discovered that the pathophysiology of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome RDS involved the insufficient. This coating is often missing or deficient in the lungs of.
NRDS is a common disease. Infants of pulmonary disability or.
/premature-baby-in-nicu-545701274-5946e5b85f9b58d58a54e7a2.jpg)
Atelectasis And Hyaline Membrane Disease In Preemies

Figure 5 From Surfactant Metabolism In The Newborn The Impact Of Ventilation Strategy And Lung Disease Semantic Scholar
Surfaxin Lucinactant Treatment For Preventing Infant Rds Clinical Trials Arena

Postnatal Steroids In Premature Babies Where Are We Now Paediatricfoam
Biophysical Study Of Lung Surfactant Laboratory Of Biocolloids And Biointerfaces

Structure Function Relationships In Pulmonary Surfactant Membranes From Biophysics To Therapy Sciencedirect
Surfactant Replacement Therapy A Milestone In Neonatology Efcni
10 Surfactant Deficiency In A Premature Infant 9 Histologic Download Scientific Diagram
Surfactant During Lung Development Chapter 8 Fetal And Neonatal Lung Development

The Fascinating Story Of Surfactant Halliday 2017 Journal Of Paediatrics And Child Health Wiley Online Library
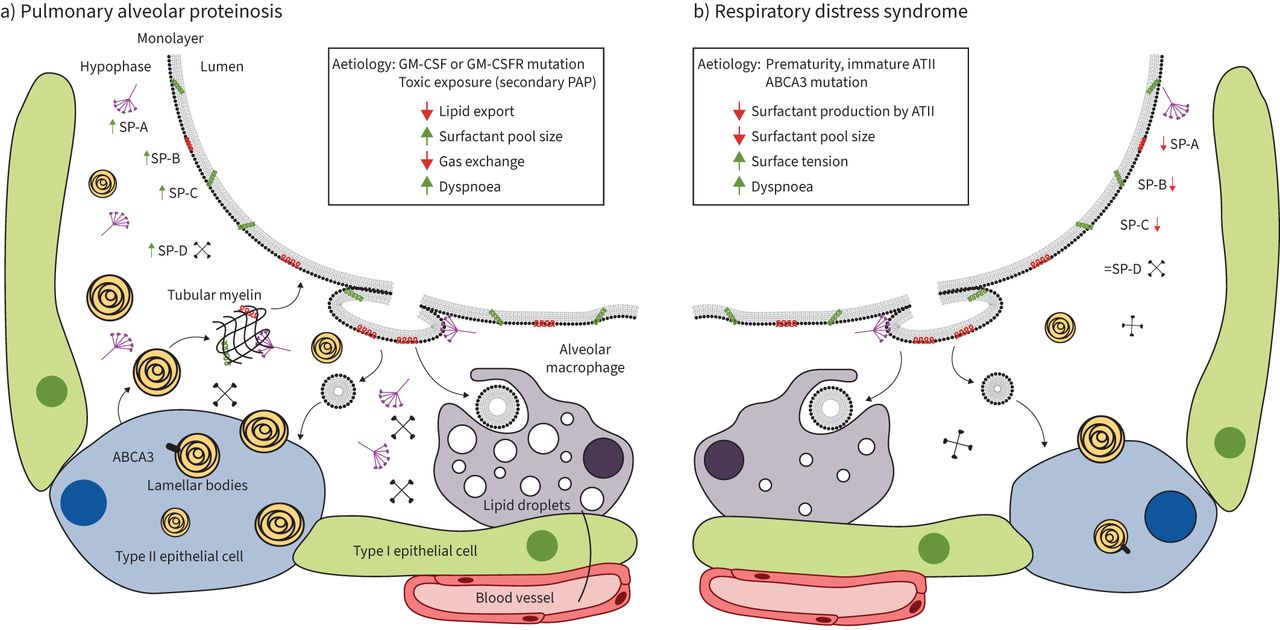
Revisiting The Role Of Pulmonary Surfactant In Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases And Environmental Exposure European Respiratory Society

Respiratory Distress Syndrome In Preterm Neonates In The Era Of Precision Medicine A Modern Critical Care Based Approach Pediatrics Neonatology
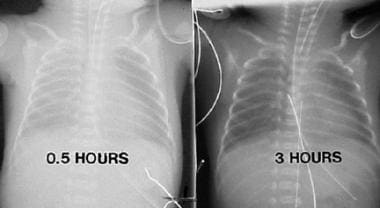
Respiratory Distress Syndrome Background Etiology Epidemiology
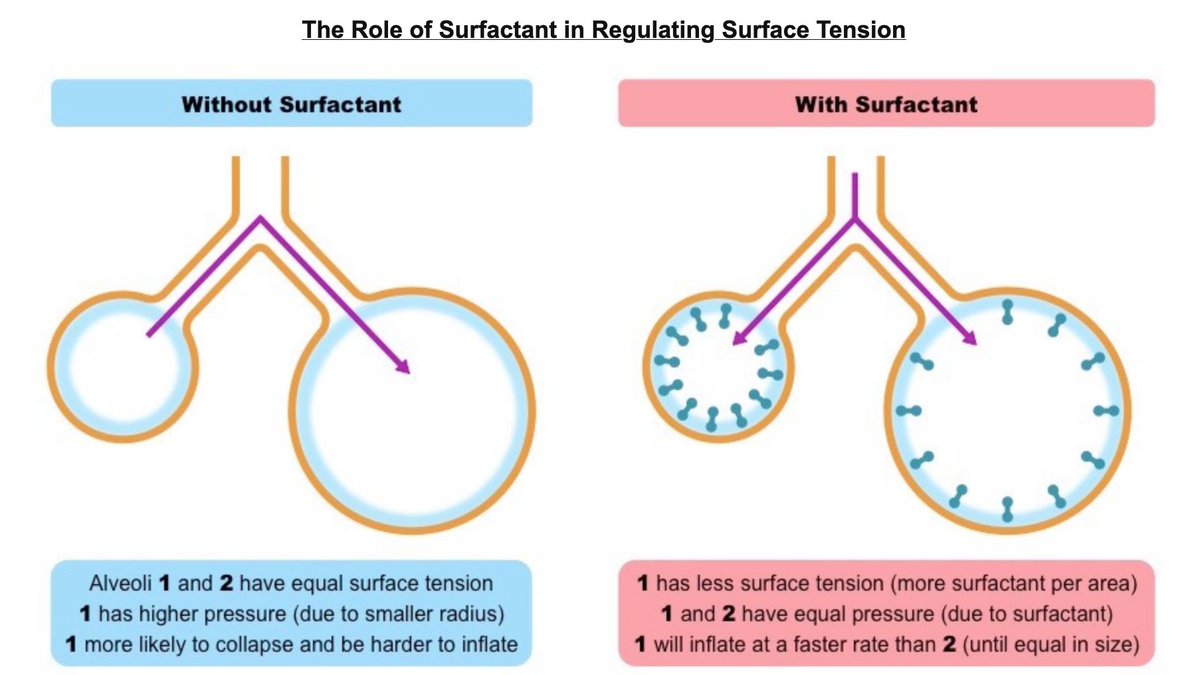
David Sinclair On Twitter Premature Infants Often Suffer From Respiratory Distress Syndrome Rds Due To Insufficient Surfactant This Is Treated Today With Surfactant Preparations Extracted From Animal Lungs E G Curosurf Infasurf Alveofact

Single Dose Surfactant Early Rescue Therapy In Respiratory Distress Syndrome Experience And Outcome At A Tertiary Care Centre Semantic Scholar

Treatment Of Breathing Problems In Premature Babies

Breathing Mismanagement Of Newborns Trusted Legal Help
Efficient Delipidation Of A Recombinant Lung Surfactant Lipopeptide Analogue By Liquid Gel Chromatography Plos One